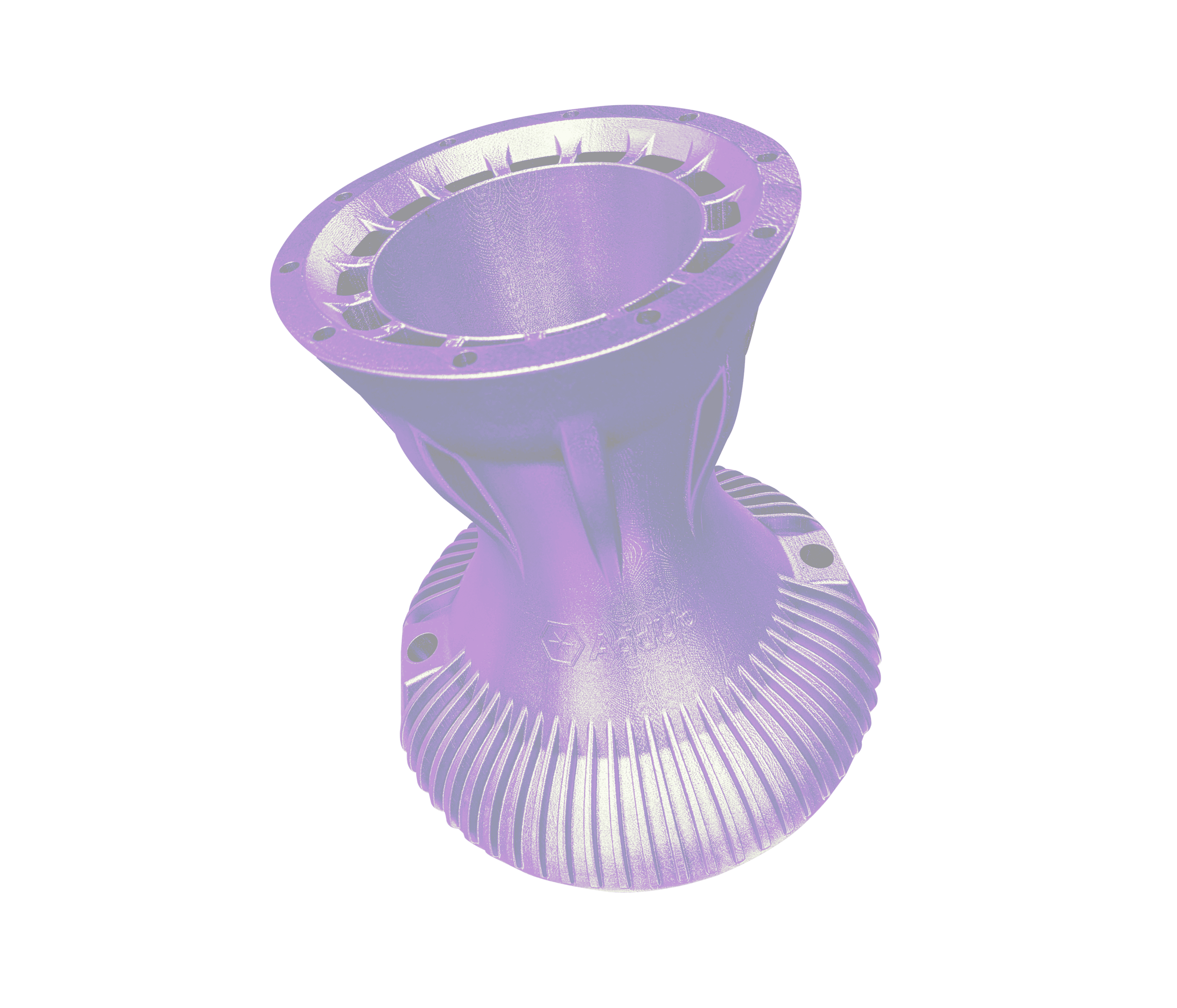
Transforming the Tooling Industry with 3D Printed Injection Molds
Additive manufacturing enables the creation of highly customized solutions for the tooling industry. Tools and molds can be tailored to specific production needs, accommodating complex geometries and features that would otherwise be impossible or costly to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods. Benefits of AM for the tooling industry include: shortened cycle time, reduced material waste, improved part performance, longer tool life and sustainability.
Tooling is in our DNA
The birth of our company was based on the need for a metal 3D printer capable of serial production on an industrial scale. Michelin needed a PBF machine to achieve resolution down to 0.2mm features, shallow overhangs as low as 15 degrees, and surface finish as low as 4 Ra µm, as printed. They partnered with industrial powerhouse, Fives, and created the FormUp 350. Today, Michelin uses AddUp’s reliable and repeatable FormUp 350 to print more than one million tire sipe molds a year.
With more than 20 years of experience in AM, AddUp’s 3D metal printers take tooling molds and dies to the next level. The FormUp 350 can be used with standard medium powder or a finer powder PSD in combination with a standard blade or roller recoater system, based on the needs of the application. For example, using a finer particle PSD and AddUp’s roller recoater technology maximizes the benefits of conformal cooling. This combination allows for design complexity while achieving best-in-class surface finish, as printed. AddUp technology also allows for extreme overhang geometry while limiting the number of support structures needed. This is important for tooling applications because the smooth finish on internal cooling channels of a mold directly affect the cycle time, part performance and overall life of the tool.
As an expert of two different additive technologies, AddUp has the unique ability to optimize tooling applications using both Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) and Directed Energy Deposition (DED). Where PBF is ideal for mold designs integrating conformal cooling, DED shines for tooling repair applications by building material atop an existing part to extend the overall life of the part.
Manufacturing Workhorse
The FormUp 350 is designed for dependability. It has been built to maximize production with minimal downtime for maintenance or turnover between different builds.
Scalable Production
We bring extensive experience scaling up to full production. AddUp machines are designed to meet an OEE level demanded for serial production.
Better Performance
Complex molds with internal conformal cooling channels to optimize part performance and tool life.
Superior Surface Finish
Our exclusive fine powder and roller recoater technology gives us best-in-class surface finishes, as printed, and allowing us to create parts with very few support structures.
Time and Cost Savings
With our machines’ ability to build parts with best-in-class surface finish “as printed”, our customers save time and money on post processing and finishing.
Open Machine Parameters
Some competitors keep the workings of their machines secret, but we don’t. Do more with our open platform by twisting and turning the knobs as you see fit.
Key Applications in the Tooling & Industrial Industries
AddUp has extensive experience in tooling applications including injection molding, extrusion dies, turbo housings, impellers and manifolds. We consider the benefits of both PBF and DED technology to provide a solution that works best for your specific application.
The FormUp 350 optimizes tooling design using conformal cooling and complex geometries otherwise impossible to create with traditional manufacturing methods. AddUp’s Modulo 400 and Magic 800 DED machines optimize production with better meltpool control and the ability to create near net shapes.
Injection Molding
Injection molding involves injecting a molten material into a mold cavity under high pressure and then allowing it to cool and solidify, resulting in the creation of a finished part with the desired shape and features. Additive manufacturing offers significant advantages for injection molding using conformal cooling and the FormUp 350 is built to maximize those benefits. Using this technology, molds can be created with cooling channels as close as possible to the mold cavity, designed to reduce hot spots and provide better durability. This provides longer tool life and faster cooling times when compared to traditionally manufactured molds. The payback for using additively manufactured molds is quickly realized through reduced production costs, materials saved, and increased cycle time providing maximum productivity.

Extrusion Die
An extrusion die is a specialized tool used in the process of extrusion, which is a manufacturing process that involves forcing a material through a shaped opening to create a shape. The FormUp 350 uses a roller recoater technology allowing for design complexity while requiring minimum or no supports and achieving a best-in-class surface finish. This maximizes the benefits of conformal cooling for extrusion dies, reducing cooling time to improve cycle time and minimizing stress therefore extending the life of the tool.

Die Casting
Die casting is a manufacturing process used to produce metal parts with intricate shapes, precise dimensions, and fine surface details. It involves injecting molten metal, typically an alloy of aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, under high pressure into a reusable mold called a “die.” The flexibility that additive manufacturing provides works well for die casting applications because it allows for fast prototyping without the time-consuming process typically required in tooling. The FormUp 350 excels at producing intricate and complex geometries often needed for die casting applications.
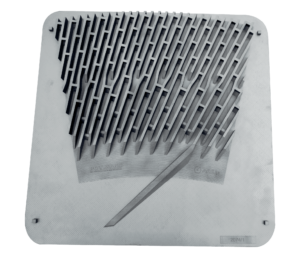
Pumps and Turbomachinery
Pumps are used to transfer fluids from one location to another by increasing the fluid’s pressure and flow rate. Additive manufacturing offers numerous advantages for turbomachinery including design flexibility and improved performance. Some of these applications require complex assemblies which can be consolidated into a single component using AM, reducing overall production costs. AM is also used for these types of applications to optimize internal structures leading to more efficient parts requiring less energy consumption.

Manifolds
A manifold is a component used for industrial applications to distribute, collect, or control the flow of fluids, gases, or other substances. Additive manufacturing allows for lightweight yet strong designs to optimize performance for these applications. AM also enables the integration of functional features directly into the manifold, such as valves, sensors, connectors, and brackets. This reduces the need for additional assembly steps and potential points of failure.

Impellers
Impellers are rotating components designed to increase or decrease the flow and pressure of a fluid in an engine. They are excellent applications for additive manufacturing thanks to the ability to create highly complex and customized blade designs to improve fluid dynamics, performance and efficiency. Thanks to the FormUp 350’s fine powder and recoater technology, these blades can be created without support structures and superior surface finish. This not only maximizes the performance of the part, but also saves on overall production costs.


5-in-1 Manifold
When DED technology allows printing parts with complex shapes without additional tooling. A Greek manufacturer Spyros Panopoulos Automotive has asked AddUp to produce 3D-printed parts, including a 5-in-1 manifold. The challenge…
Extrusion Die
This study explores the use of additive manufacturing, specifically Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), to create extrusion dies with improved performance and cooling capabilities. History Extrusion is a popular manufacturing method for parts…

TOOLING
Grinding System Coolant Nozzle
A one-piece optimized coolant nozzle that delivers coolant flow into precise locations. The nozzle was officially installed grinding machine, optimizing its performance. History Fives is an international industrial engineering group with over 200+…
Hydraulic Block
Hydraulic blocks are present in most machines and devices, throughout a variety of industries. In the case of this hydraulic block, the entire part is 3D printed in a single…
Impeller Wheel
This case study explores the feasibility of using additive manufacturing, specifically the Form Up 350 PBF machine, to produce over 100,000 Impeller wheels annually for Ford, replacing traditional machining techniques. History Ford…

Injection Mold
See how to improve the cooling of the inserts on a mold using additive technology while increasing the mold’s performance and decreasing the cycle time. Short injection times are crucial for…
Michelin Tires Sipes
Discover how Michelin produces over one million tire sipes a year for their production molds using metal 3D printing When Michelin found that the metal AM machines on the market did not meet their high-quality…
Orano Manifold Spare Part
The goal of the project is to verify the technical and economic feasibility of additive manufacturing of complex geometric replacement parts for equipment that is no longer manufactured. The project aims…

Schneider Inductor
See how this 3D printed inductor has met all quality specifications, and its industrial performance has surpassed initial expectations. An induction heating coil is a production tool that allows performing a…
Siebenwurst Injection Mold
This case study explores the benefits of using 3D printed injection molds with optimized cooling channels. The project between Siebenwurst and AddUp aimed to improve productivity and quality in the…
Materials used in Tooling & Industrial Applications
Due to the nature of the applications, the tooling industry utilizes materials that are hard, durable and can withstand extreme temperatures. In some applications, it is also important for the material to be corrosion resistant.
Maraging 300
Maraging 300 is a steel often used in die-casting applications due to its great combination of impact resistance and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures.
AISI 420
AISI 420 is a stainless steel commonly used to manufacture molds for plastic injection molding. It has both high mechanical strength and good corrosion resistance.
AlSi7Mg0.6
AlSi7Mg0.6 is a lightweight material commonly used in aerospace and industrial applications. Its low weight combined with design benefits of using additive manufacturing (i.e. increased geometric complexities and topology optimization) can greatly increase the range of use applications.
AlSi10Mg
AlSi10Mg is a Al-Si based alloy with good mechanical properties and thermal conductivity. It is a suitable materials for applications requiring low weight, high strength and load bearing components. It is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
INDUSTRIAL MACHINES
With more than 20 years experience in Additive Manufacturing, our machines have been designed to master detail and optimize productivity.

SMART SOFTWARE
AddUp is leading the way with in-process monitoring, providing confidence part quality with a full suite of quality assurance monitoring software to lessen, or even eliminate, the need for rigorous testing after a part is printed. From part preparation to simulation, monitoring, and production, every link of the AddUp digital chain offers a high level of performance with user-friendly software.

Get Started with AddUp
Realize the potential digital manufacturing has to offer. Get started with AddUp and learn how AM delivers innovative solutions to solve manufacturers toughest challenges.